
- 阻害剤
- 研究分野別
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Epigenetics
- Methylation
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis
- Autophagy
- ER stress & UPR
- JAK/STAT
- MAPK
- Cytoskeletal Signaling
- Cell Cycle
- TGF-beta/Smad
- 化合物ライブラリー
- Popular Compound Libraries
- Customize Library
- Clinical and FDA-approved Related
- Bioactive Compound Libraries
- Inhibitor Related
- Natural Product Related
- Metabolism Related
- Cell Death Related
- By Signaling Pathway
- By Disease
- Anti-infection and Antiviral Related
- Neuronal and Immunology Related
- Fragment and Covalent Related
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-II
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Alkaloid Compound LibraryNew
- Angiogenesis Related compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Anti-alzheimer Disease Compound Library
- Antibiotics compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound Library
- Anti-diabetic Compound Library
- Anti-infection Compound Library
- Antioxidant Compound Library
- Anti-parasitic Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Calcium Channel Blocker LibraryNew
- Cambridge Cancer Compound Library
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Cell Cycle compound library
- CNS-Penetrant Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- Cytokine Inhibitor LibraryNew
- Cytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library
- Drug-like Compound Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Epigenetics Compound Library
- Exosome Secretion Related Compound LibraryNew
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Ferroptosis Compound Library
- Flavonoid Compound Library
- Fragment Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- Glycolysis Compound Library
- GPCR Compound Library
- Gut Microbial Metabolite Library
- HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- Histone modification compound library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Human Hormone Related Compound LibraryNew
- Human Transcription Factor Compound LibraryNew
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Inhibitor Library
- Ion Channel Ligand Library
- JAK/STAT compound library
- Lipid Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Macrocyclic Compound Library
- MAPK Inhibitor Library
- Medicine Food Homology Compound Library
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Methylation Compound Library
- Mouse Metabolite Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Organic Compound Library
- Neuronal Signaling Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Nucleoside Analogue Library
- Obesity Compound Library
- Oxidative Stress Compound LibraryNew
- Phenotypic Screening Library
- PI3K/Akt Inhibitor Library
- Protease Inhibitor Library
- Protein-protein Interaction Inhibitor Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Small Molecule Immuno-Oncology Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Differentiation Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Phenol Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Terpenoid Compound LibraryNew
- TGF-beta/Smad compound library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Library
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Ubiquitination Compound Library
-
Cherry Picking
You can personalize your library with chemicals from within Selleck's inventory. Build the right library for your research endeavors by choosing from compounds in all of our available libraries.
Please contact us at info@selleck.co.jp to customize your library.
You could select:
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-II
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Metabolism Compound Library
- 抗体
- 新製品
- お問い合わせ
Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1)
Thiamine or vitamin B1 is a water-soluble vitamin of the B complex, its phosphate derivatives are involved in many cellular processes.
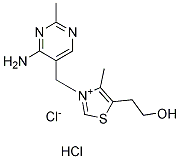
CAS No. 67-03-8
文献中Selleckの製品使用例(2)
Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1)関連製品
Vitamin阻害剤の選択性比較
| 阻害剤 | Citation | VEGFR1 | VEGFR2 | VEGFR3 | VEGFR | VEGF | その他 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foretinib | 93 | Met,Tie-2,RON | |||||
| Cediranib (AZD2171) | 67 | c-Kit,PDGFRβ,FGFR1 | |||||
| PD173074 | 123 | FGFR1 | |||||
| Dovitinib (TKI-258) | 51 | FLT3,c-Kit,FGFR1 | |||||
| Linifanib (ABT-869) | 33 | CSF-1R,FLT3,Kit | |||||
| Vatalanib (PTK787) 2HCl | 52 | PDGFRβ,c-Kit,c-Fms | |||||
| RAF265 (CHIR-265) | 23 | B-Raf | |||||
| Motesanib Diphosphate (AMG-706) | 12 | Kit,RET,PDGFR |
もっと見る
1. "+" indicates inhibitory effect. Increased inhibition is marked by a higher "+" designation. 2. "✔" indicates inhibitory effect, but without specific value.
生物活性
| 製品説明 | Thiamine or vitamin B1 is a water-soluble vitamin of the B complex, its phosphate derivatives are involved in many cellular processes. |
|---|
| In Vitro | ||||
| In vitro | Thiamine (50 mM), in addition to its nutritional value, induces systemic acquired resistance (SAR) in rice, tobacco, cucumber, and Arabidopsis. Thiamine-treated rice, Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), and vegetable crop plants shows resistance to fungal, bacterial, and viral infections. Thiamine treatment induces the transient expression of pathogenesis-related (PR) genes in rice and other plants. In addition, Thiamine treatment potentiates stronger and more rapid PR gene expression and the up-regulation of protein kinase C activity. [1] Vitamin B1 (10 μM) prevents acetaldehyde-induced inhibition of myocyte shortening in adult rat ventricular myocytes. Vitamin B1 (10 μM) effectively blunts the acetaldehyde-induced depression in ±dL/dt in adult rat ventricular myocytes. Vitamin B1 (10 μM) prevents acetaldehyde-induced shortening of time-to-peak shortening in adult rat ventricular myocytes. Vitamin B1 (10 μM) prevents acetaldehyde-induced elevation in both protein carbonyl formation and caspase-3 activation in adult rat ventricular myocytes. [2] Thiamine uptake is energy- and temperature-dependent, pH-sensitive, Na+-independent, saturable at both the nanomolar (apparent Km, 30 nM) and the micromolar (apparent Km, 1.72 mM) concentration ranges in ARPE-19 cells. Uptake of Thiamine is adaptively regulated by extracellular substrate level via transcriptionally mediated mechanisms that involve both hTHTR-1 and hTHTR-2 in ARPE-19 cells, it is also regulated by an intracellular Ca2+-calmodulin-mediated pathway. [3] Thiamine-responsive megaloblastic anemia (TRMA) fibroblasts are rescued from death with 10 nM-30 nM Thiamine (in the range of normal plasma thiamine concentrations). Normal fibroblasts exhibits saturable, high-affinity thiamine uptake (Km 400 nM-550 nM; Vmax 11 pmol/min/1×106 cells), while TRMA fibroblasts lacks detectable high-affinity uptake. At 30 nM Thiamine, the rate of uptake of Thiamine by TRMA fibroblasts is 10-fold less than that of wild-type, which explains the increased apoptosis of TRMA fibroblasts. [4] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 実験結果図 | Methods | Biomarkers | 結果図 | PMID |
| Western blot | THICL / THICS / THI4L / THI4M / THI4S / ACT Bax / Bid / p53 / p84 Rpb1 / Fcp1 / f-Rpb3 / Tfg3 / Rpb7 / Rpb4 |
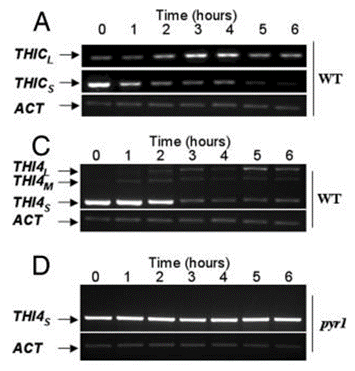
|
18093957 | |
| Growth inhibition assay | TEN1 and TEAEN1 strains hippocampal Dcx+ cells |
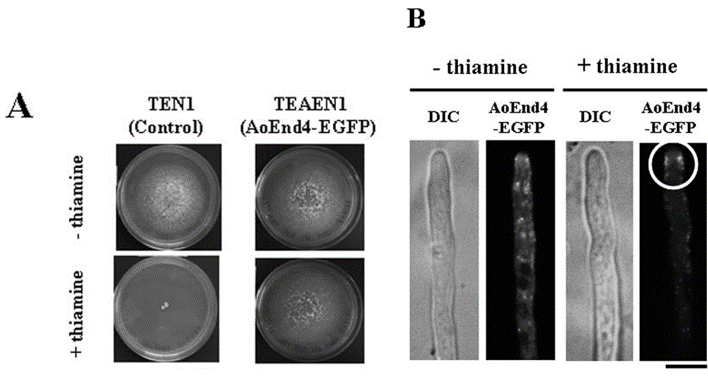
|
19028995 | |
| Glycolysis stress test | Glycolysis stress |
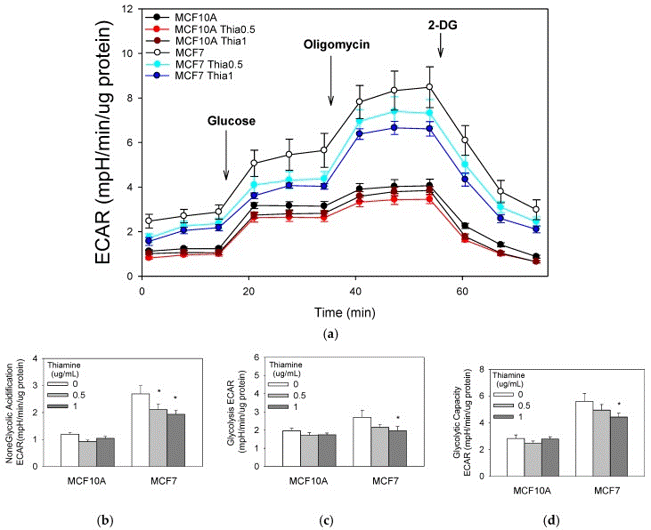
|
29914147 | |
| Cell death | Cell survival |
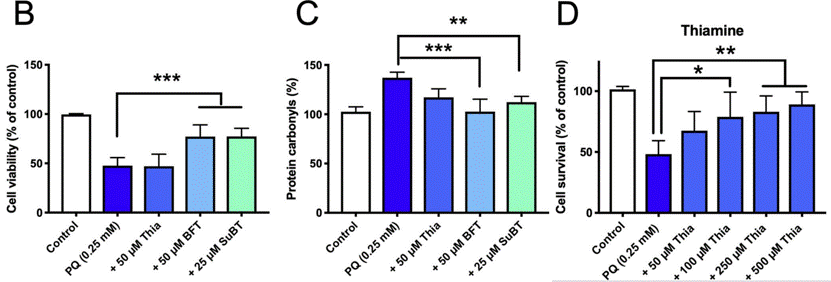
|
31193162 | |
| Western blot / RNA Blot | PR-1 / rRNA PR-1 / rRNA |
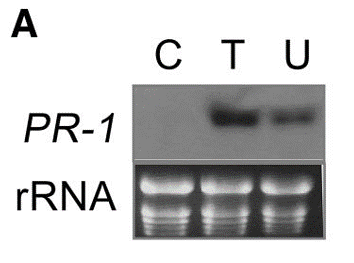
|
15980201 | |
| Immunofluorescence | Thi76KR / Thi7M399R / ThiN350K |
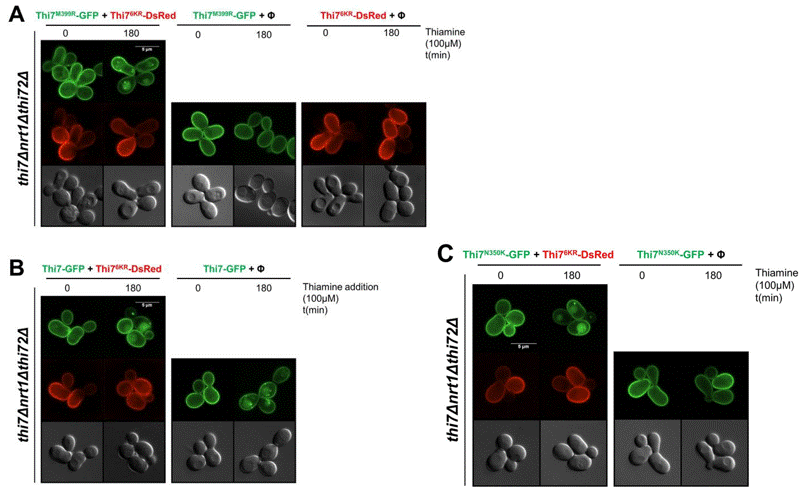
|
31658248 | |
| In Vivo | ||
| In Vivo | Thiamine deficiency results in amyloid precursor protein immunoreactivity accumulated in swollen neurites within, or around lesions in rats, or in abnormal clusters in mice. [5] | |
|---|---|---|
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT06298344 | Recruiting | Congenital Heart Disease|Thiamine Deficiency|Patent Ductus Arteriosus|Ventricular Septal Defect|Atrial Septal Defect |
Universitas Sumatera Utara |
May 1 2024 | Early Phase 1 |
| NCT06326996 | Not yet recruiting | Coronary Heart Disease|Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting |
University of California Los Angeles |
May 2024 | Not Applicable |
| NCT06322212 | Not yet recruiting | Type2diabetes |
University of California Los Angeles |
April 2024 | Not Applicable |
| NCT06323538 | Not yet recruiting | Dietary Exposure|Diabetes Mellitus Type 2|Cardiovascular Diseases|Bone Loss|Sustainability|Exposure|Obesity|Vitamin Deficiency|Mineral Deficiency |
German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment|Max Rubner-Institut|University of Bonn|Research Institute for Plant-Based Nutrition|University of Jena|University of Regensburg|Heidelberg University|University of Vienna |
April 1 2024 | -- |
化学情報
| 分子量 | 337.27 | 化学式 | C12 H17N4OS.HCl |
| CAS No. | 67-03-8 | SDF | Download Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) SDFをダウンロードする |
| Smiles | CC1=C(SC=[N+]1CC2=CN=C(N=C2N)C)CCO.Cl.[Cl-] | ||
| 保管 | |||
|
In vitro |
Water : 67 mg/mL DMSO : Insoluble ( 吸湿したDMSOは溶解度を減少させます。新しいDMSOをご使用ください。) Ethanol : Insoluble |
モル濃度計算器 |
実験計算
投与溶液組成計算機(クリア溶液)
ステップ1:実験データを入力してください。(実験操作によるロスを考慮し、動物数を1匹分多くして計算・調製することを推奨します)
mg/kg
g
μL
匹
ステップ2:投与溶媒の組成を入力してください。(ロット毎に適した溶解組成が異なる場合があります。詳細については弊社までお問い合わせください)
% DMSO
%
% Tween 80
% ddH2O
%DMSO
%
計算結果:
投与溶媒濃度: mg/ml;
DMSOストック溶液調製方法: mg 試薬を μL DMSOに溶解する(濃度 mg/mL, 注:濃度が当該ロットのDMSO溶解度を超える場合はご連絡ください。 )
投与溶媒調製方法:Take μL DMSOストック溶液に μL PEG300,を加え、完全溶解後μL Tween 80,を加えて完全溶解させた後 μL ddH2O,を加え完全に溶解させます。
投与溶媒調製方法:μL DMSOストック溶液に μL Corn oil,を加え、完全溶解。
注意:1.ストック溶液に沈殿、混濁などがないことをご確認ください;
2.順番通りに溶剤を加えてください。次のステップに進む前に溶液に沈殿、混濁などがないことを確認してから加えてください。ボルテックス、ソニケーション、水浴加熱など物理的な方法で溶解を早めることは可能です。
技術サポート
ストックの作り方、阻害剤の保管方法、細胞実験や動物実験の際に注意すべき点など、製品を取扱う時に問い合わせが多かった質問に対しては取扱説明書でお答えしています。
他に質問がある場合は、お気軽にお問い合わせください。
* 必須
Tags: Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1)を買う | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) ic50 | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1)供給者 | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1)を購入する | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1)費用 | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1)生産者 | オーダーThiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1)化学構造 | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1)分子量 | Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1)代理店
