
- 阻害剤
- 研究分野別
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Epigenetics
- Methylation
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis
- Autophagy
- ER stress & UPR
- JAK/STAT
- MAPK
- Cytoskeletal Signaling
- Cell Cycle
- TGF-beta/Smad
- 化合物ライブラリー
- Popular Compound Libraries
- Customize Library
- Clinical and FDA-approved Related
- Bioactive Compound Libraries
- Inhibitor Related
- Natural Product Related
- Metabolism Related
- Cell Death Related
- By Signaling Pathway
- By Disease
- Anti-infection and Antiviral Related
- Neuronal and Immunology Related
- Fragment and Covalent Related
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-II
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Alkaloid Compound LibraryNew
- Angiogenesis Related compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Anti-alzheimer Disease Compound Library
- Antibiotics compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound Library
- Anti-diabetic Compound Library
- Anti-infection Compound Library
- Antioxidant Compound Library
- Anti-parasitic Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Calcium Channel Blocker LibraryNew
- Cambridge Cancer Compound Library
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Cell Cycle compound library
- CNS-Penetrant Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- Cytokine Inhibitor LibraryNew
- Cytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library
- Drug-like Compound Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Epigenetics Compound Library
- Exosome Secretion Related Compound LibraryNew
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Ferroptosis Compound Library
- Flavonoid Compound Library
- Fragment Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- Glycolysis Compound Library
- GPCR Compound Library
- Gut Microbial Metabolite Library
- HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- Histone modification compound library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Human Hormone Related Compound LibraryNew
- Human Transcription Factor Compound LibraryNew
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Inhibitor Library
- Ion Channel Ligand Library
- JAK/STAT compound library
- Lipid Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Macrocyclic Compound Library
- MAPK Inhibitor Library
- Medicine Food Homology Compound Library
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Methylation Compound Library
- Mouse Metabolite Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Organic Compound Library
- Neuronal Signaling Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Nucleoside Analogue Library
- Obesity Compound Library
- Oxidative Stress Compound LibraryNew
- Phenotypic Screening Library
- PI3K/Akt Inhibitor Library
- Protease Inhibitor Library
- Protein-protein Interaction Inhibitor Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Small Molecule Immuno-Oncology Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Differentiation Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Phenol Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Terpenoid Compound LibraryNew
- TGF-beta/Smad compound library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Library
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Ubiquitination Compound Library
-
Cherry Picking
You can personalize your library with chemicals from within Selleck's inventory. Build the right library for your research endeavors by choosing from compounds in all of our available libraries.
Please contact us at info@selleck.co.jp to customize your library.
You could select:
- 抗体
- 新製品
- お問い合わせ
Quinolinic acid
別名:pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid, QUIN
Quinolinic Acid (pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid, QUIN), a neuroactive metabolite of the kynurenine pathway, is an agonist of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor.
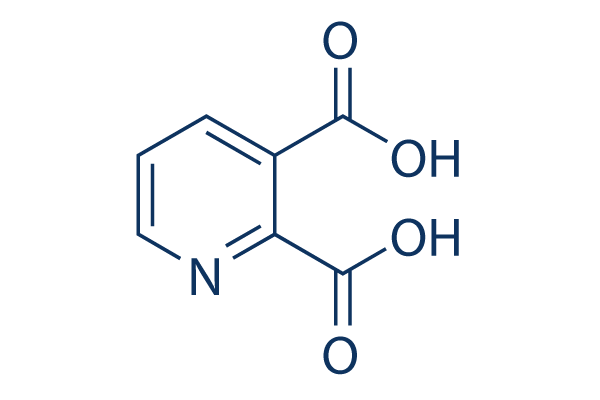
CAS No. 89-00-9
製品安全説明書
現在のバッチを見る:
S362401
DMSO]
25 mg/mL]
false]
Water]
3 mg/mL]
false]
Ethanol]
Insoluble]
false
純度:
99.16%
99.16
Quinolinic acid関連製品
NMDAR阻害剤の選択性比較
生物活性
| 製品説明 | Quinolinic Acid (pyridine-2,3-dicarboxylic acid, QUIN), a neuroactive metabolite of the kynurenine pathway, is an agonist of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor. | |
|---|---|---|
| Targets |
|
| In Vitro | ||||
| In vitro | QUIN is an agonist of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, and it has a high in vivo potency as an excitotoxin. Although QUIN has an uptake system, its neuronal degradation enzyme is rapidly saturated, and the rest of extracellular QUIN can continue stimulating the NMDA receptor. QUIN (10 μM) prevents of glutamate-induced excitotoxicity in primary cultures of rat cerebellar granule neurons, nevertheless mature organotypic cultures of rat corticostriatal system or caudate nucleus chronically exposed to 100 nM QUIN for up to 7 weeks show focal degeneration characterized by the presence of vacuoles in neuropil, swollen dendrites, occasional swollen post-synaptic elements, and degenerated neurons. In vitro QUIN treatment of human primary foetal neurons leads to a substantial increase of tau phosphorylation at multiple positions. The increase in QUIN-induced phosphorylation of tau is attributed to a decrease in the expression and activity of the major tau phosphatases. QUIN can inhibit B monoamine oxidase (MAO-B) in human brain synaptosomal mitochondria and also can be a potent inhibitor of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (EC 4.1.1.32) from rat liver cytoplasm, an important enzyme in the gluconeogenesis pathway that converts oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate. QUIN can increase free radical production by inducing NOS activity in astrocytes and neurons, leading to oxidative stress, increasing both poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) activity and extracellular lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity[1]. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | ||
| In Vivo | Quinolinic acid (QUIN), a neuroactive metabolite of the kynurenine pathway, is normally presented in nanomolar concentrations in human brain and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and is often implicated in the pathogenesis of a variety of human neurological diseases. The concentration of QUIN varies among different brain regions, with the cerebral cortex containing approximately 1.8 nmol/g wet weight; almost 2-fold than that found in the hippocampus (1 nmol/g wet weight). Intraarterial administration of either micromolar or millimolar concentrations of QUIN results in only negligible accumulations of this metabolite in the brain, suggesting that the central nervous system (CNS) appears to be well protected by the blood brain barrier (BBB) from peripheral QUIN. QUIN can also increase glutamate release and inhibit its reuptake by astrocytes, thus increasing its concentration in the microenvironments, causing neurotoxicity and also limiting glutamate to glutamine recycling in astrocytes by decreasing glutamine synthetase activity. Intrastriatal injection of QUIN provokes a decrease of cellular respiration and ATP levels[1]. | |
|---|---|---|
| 動物実験 | 動物モデル | C57Bl/6J mice |
| 投与量 | 30 nmol | |
| 投与経路 | Intracerebral injection | |
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05513807 | Not yet recruiting | Delayed Graft Function |
Assistance Publique - Hôpitaux de Paris|Institut National de la Santé Et de la Recherche Médicale France|Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique France |
November 2022 | Phase 3 |
| NCT05718310 | Recruiting | Migraine|Migraine Disorders|Pain |
IRCCS National Neurological Institute C. Mondino Foundation|University of Pavia |
November 1 2022 | Not Applicable |
| NCT05969990 | Recruiting | Migraine in Children |
Qilu Hospital of Shandong University |
January 1 2022 | -- |
| NCT04342975 | Completed | AKI |
Mayo Clinic|Elysium Health |
December 1 2020 | Phase 2 |
|
化学情報
| 分子量 | 167.12 | 化学式 | C7H5NO4 |
| CAS No. | 89-00-9 | SDF | Download Quinolinic acid SDFをダウンロードする |
| Smiles | C1=CC(=C(N=C1)C(=O)O)C(=O)O | ||
| 保管 | |||
|
In vitro |
DMSO : 25 mg/mL ( (149.59 mM); 吸湿したDMSOは溶解度を減少させます。新しいDMSOをご使用ください。) Water : 3 mg/mL Ethanol : Insoluble |
モル濃度計算器 |
|
in vivo Add solvents to the product individually and in order. |
投与溶液組成計算機 | |||||
実験計算
投与溶液組成計算機(クリア溶液)
ステップ1:実験データを入力してください。(実験操作によるロスを考慮し、動物数を1匹分多くして計算・調製することを推奨します)
mg/kg
g
μL
匹
ステップ2:投与溶媒の組成を入力してください。(ロット毎に適した溶解組成が異なる場合があります。詳細については弊社までお問い合わせください)
% DMSO
%
% Tween 80
% ddH2O
%DMSO
%
計算結果:
投与溶媒濃度: mg/ml;
DMSOストック溶液調製方法: mg 試薬を μL DMSOに溶解する(濃度 mg/mL, 注:濃度が当該ロットのDMSO溶解度を超える場合はご連絡ください。 )
投与溶媒調製方法:Take μL DMSOストック溶液に μL PEG300,を加え、完全溶解後μL Tween 80,を加えて完全溶解させた後 μL ddH2O,を加え完全に溶解させます。
投与溶媒調製方法:μL DMSOストック溶液に μL Corn oil,を加え、完全溶解。
注意:1.ストック溶液に沈殿、混濁などがないことをご確認ください;
2.順番通りに溶剤を加えてください。次のステップに進む前に溶液に沈殿、混濁などがないことを確認してから加えてください。ボルテックス、ソニケーション、水浴加熱など物理的な方法で溶解を早めることは可能です。
技術サポート
ストックの作り方、阻害剤の保管方法、細胞実験や動物実験の際に注意すべき点など、製品を取扱う時に問い合わせが多かった質問に対しては取扱説明書でお答えしています。
他に質問がある場合は、お気軽にお問い合わせください。
* 必須
